Image Analysis
Examiner and lecturer
Josef Bigun
Laboratory Exercises:
Laborartory Exercises are implemented in
Matlab.
If you feel that you lack adequate
knowledge in Matlab or would like to brush up your knowledge, you might find the
link lab0 useful. Please
note that lab0 and other exercises cited therein are voluntary and
there is no instruction opportunity scheduled for them.
The labs of the course comprise lab1 through lab10, only. For each
lab exercise, two hours of time is scheduled (with the lab-leader) in a
laboratory, equiped with adequate computers in the campus area (see
schedule below). Participants will need to have own (normal student)
accounts to participate to lab-exercises.
Litterature:
[1] J. Bigun, "Vision
with direction", Springer, (2006).
[2] Laboratory exercises are in Matlab
Exercise_1,
Exercise_2,
Exercise_3,
Exercise_4,
Exercise_5,
Exercise_6,
Exercise_7,
Exercise_8,
Exercise_9,
Exercise_10
Course Contents:
The course consists in two parts: Fundamentals of Image Analysis (in
2D) and Scientific Paper. Examinations of the two parts are
independent.
Fundamentals of Image analysis
Contents
 Signal representation
Signal representation
Lab1 & Lab2
 Hilbert space,
Schwarz inequality (Ch. 1-3)
Hilbert space,
Schwarz inequality (Ch. 1-3)
 Fourier
Coefficients (FC), Parseval relationship, Hermitian symmetry of
FC. (Ch. 4-5)
Fourier
Coefficients (FC), Parseval relationship, Hermitian symmetry of
FC. (Ch. 4-5)
 Fourier Transform
(FT) of continuous functions. (Ch. 6.1-6.2)
Fourier Transform
(FT) of continuous functions. (Ch. 6.1-6.2)
 Discrete Fourier
Transform (DFT), Circular topology of DFT. (Ch. 6.3-6.4).
Discrete Fourier
Transform (DFT), Circular topology of DFT. (Ch. 6.3-6.4).
Lab3 & Lab4
 Properties of FT
(DFT and FC): FT of box function, Conservation of Scalar Product,
Convolution (Ch. 7.1, 7.2, 7.3 )
Properties of FT
(DFT and FC): FT of box function, Conservation of Scalar Product,
Convolution (Ch. 7.1, 7.2, 7.3 )
 Convolution with
separable filters, Translation under FT,
FT of Gaussian function (Ch. 7.4, 7.7, Table 7.1)
Convolution with
separable filters, Translation under FT,
FT of Gaussian function (Ch. 7.4, 7.7, Table 7.1)
 Signal
representation and sampling, Interpolation functions, Derivation,
Gaussians as interpolators (Ch. 8.1, 8.2, Ch. 9.2 )
Signal
representation and sampling, Interpolation functions, Derivation,
Gaussians as interpolators (Ch. 8.1, 8.2, Ch. 9.2 )
 Multi-resolution
analysis and coarseness
Multi-resolution
analysis and coarseness
Lab5
 Gaussian & Laplacian pyramid Ch. 9.1-9.5
Gaussian & Laplacian pyramid Ch. 9.1-9.5
 Color
Color
Lab6
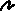 Natural color images
Ch. 2.1-2.2, Ch. 2.4-2.6
Natural color images
Ch. 2.1-2.2, Ch. 2.4-2.6
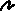 Representing
artificial data by color images, especially "angle" data (See Laboratory exercise material and lecture slides)
Representing
artificial data by color images, especially "angle" data (See Laboratory exercise material and lecture slides)
 Texture & Orientation
Texture & Orientation
Lab7
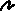 Structure
tensor and local orientation Ch. 10.1-10.8, Ch.10.11
Structure
tensor and local orientation Ch. 10.1-10.8, Ch.10.11
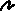 Color display of
orientation and its use as texture feature (See lab material)
Color display of
orientation and its use as texture feature (See lab material)
 Shape in binary images
Shape in binary images
Lab8
 Histograms & Binarization,
Ch. 16.1 (and lab material)
Histograms & Binarization,
Ch. 16.1 (and lab material)
 Simple shape
parameters: Area, Perimeter, Circularity, Bounding box, Area moments;
First paragraph of Ch. 17.2; Ch. 17.3, 17.4, and Equations. 17.19-17.22
Simple shape
parameters: Area, Perimeter, Circularity, Bounding box, Area moments;
First paragraph of Ch. 17.2; Ch. 17.3, 17.4, and Equations. 17.19-17.22
 Systematic
approximation of boundary curves, Fourier descriptors Ch. 17.5
including Equation 17.41
Systematic
approximation of boundary curves, Fourier descriptors Ch. 17.5
including Equation 17.41
Lab9
 Recognition of
binary shape by Fourier descriptors. Equation 17.42 until the
end of Ch. 17
Recognition of
binary shape by Fourier descriptors. Equation 17.42 until the
end of Ch. 17
Lab10
 Morphological
operators: Erosion,
Dilation, Thinning, opening, closing, inner and outer boundaries
Ch. 17.1 until Equation 17.6
Morphological
operators: Erosion,
Dilation, Thinning, opening, closing, inner and outer boundaries
Ch. 17.1 until Equation 17.6
 Pattern
matching: Hit-Miss function (Last topic in Ch. 17.1)
Pattern
matching: Hit-Miss function (Last topic in Ch. 17.1)
Scientific paper
As part of the course, the student will be asked to study a
scientific paper, which will be evaluated by an exam of its own to result either in Pass or Fail.
![]() Hilbert space,
Schwarz inequality (Ch. 1-3)
Hilbert space,
Schwarz inequality (Ch. 1-3) ![]() Fourier
Coefficients (FC), Parseval relationship, Hermitian symmetry of
FC. (Ch. 4-5)
Fourier
Coefficients (FC), Parseval relationship, Hermitian symmetry of
FC. (Ch. 4-5)
![]() Fourier Transform
(FT) of continuous functions. (Ch. 6.1-6.2)
Fourier Transform
(FT) of continuous functions. (Ch. 6.1-6.2)
![]() Discrete Fourier
Transform (DFT), Circular topology of DFT. (Ch. 6.3-6.4).
Discrete Fourier
Transform (DFT), Circular topology of DFT. (Ch. 6.3-6.4).
![]() Properties of FT
(DFT and FC): FT of box function, Conservation of Scalar Product,
Convolution (Ch. 7.1, 7.2, 7.3 )
Properties of FT
(DFT and FC): FT of box function, Conservation of Scalar Product,
Convolution (Ch. 7.1, 7.2, 7.3 ) ![]() Convolution with
separable filters, Translation under FT,
FT of Gaussian function (Ch. 7.4, 7.7, Table 7.1)
Convolution with
separable filters, Translation under FT,
FT of Gaussian function (Ch. 7.4, 7.7, Table 7.1)
![]() Signal
representation and sampling, Interpolation functions, Derivation,
Gaussians as interpolators (Ch. 8.1, 8.2, Ch. 9.2 )
Signal
representation and sampling, Interpolation functions, Derivation,
Gaussians as interpolators (Ch. 8.1, 8.2, Ch. 9.2 )